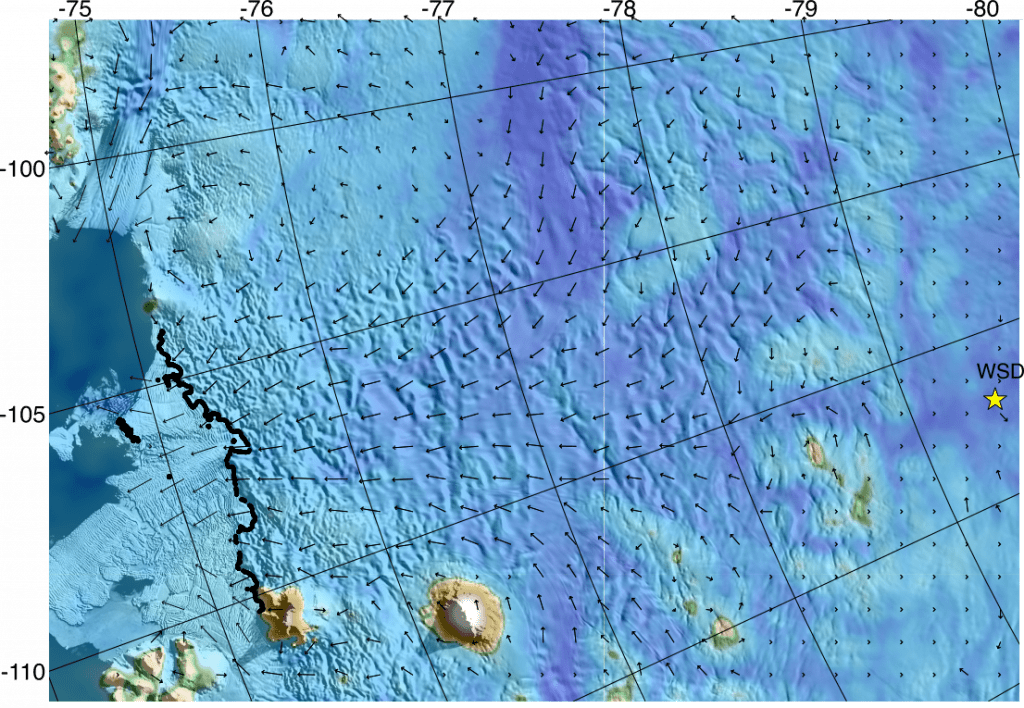
Thwaites Glacier is one of the largest glaciers in Antarctica. Like many glaciers in West Antarctica, it is grounded below sea level and the bed becomes deeper farther from the coast (a reverse bed slope). What that means is is that Thwaites is vulnerable to rapid /grounding-line retreat/ in response to a warming ocean.
We are conducting numerical modeling, satellite and airborne remote sensing data analysis, and ground-based geophysical measurements to better project Thwaites Glacier’s potential contribution to sea level rise over the coming decades and centuries.